Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
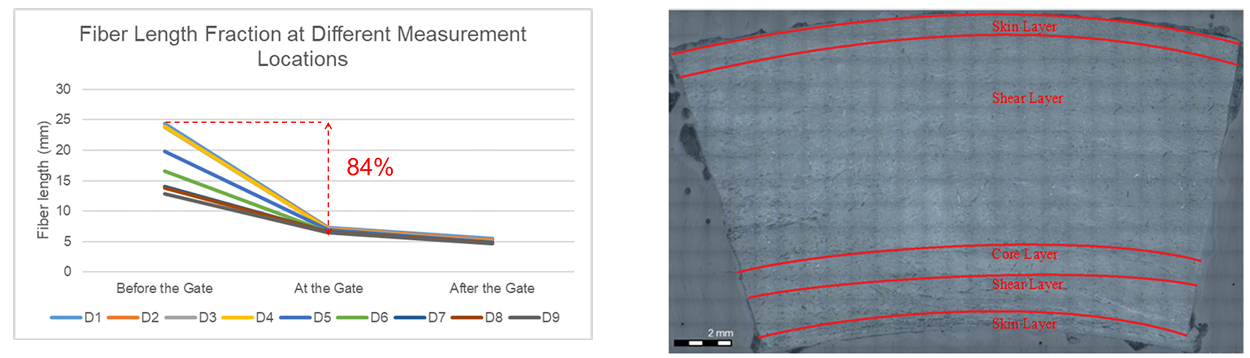
The research focuses on the fiber behavior following injection molding on a spiral-flow mold, particularly its fiber orientation behavior. The behavior of the glass fiber will be examined by altering key experiment settings, the screw speed and the back pressure, and employing different melt paths. The results show that the application of high back pressure and high screw speed decreased the fiber length but successfully increased the fiber orientation average to the flow direction. The desig... Read more
Ahmad Hafizh Ridho, Feng-Jung Cheng, Sheng-Jye Hwang
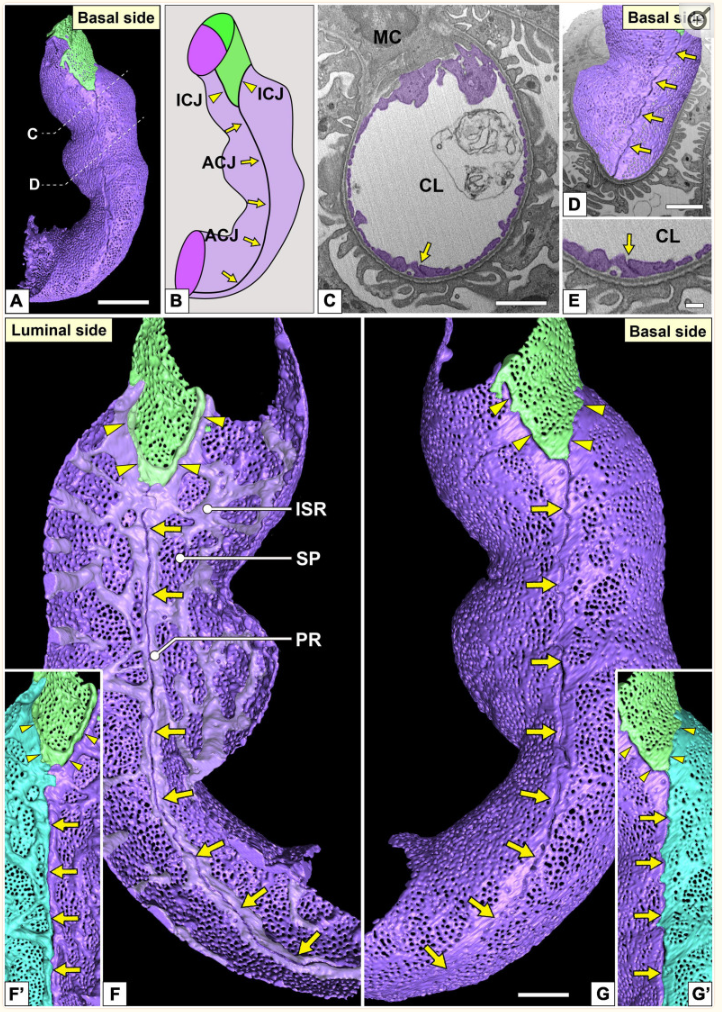
Three-Dimensional Architecture of Glomerular Endothelial Cells Revealed by FIB-SEM Tomography
Focused-ion beam-scanning electron microscopic (FIB-SEM) tomography enables easier acquisition of a series of ultrastructural, sectional images directly from resin-embedded biological samples. In this study, to clarify the three-dimensional (3D) architecture of glomerular endothelial cells (GEnCs) in adult rats, we manually extracted GEnCs from serial FIB-SEM images and reconstructed them on an Amira reconstruction software. The luminal and basal surface structures were clearly visualized in ... Read more
Yuto Kawasaki, Yasue Hosoyamada, Takayuki Miyaki, Junji Yamaguchi, Soichiro Kakuta, Tatsuo Sakai, and Koichiro Ichimura
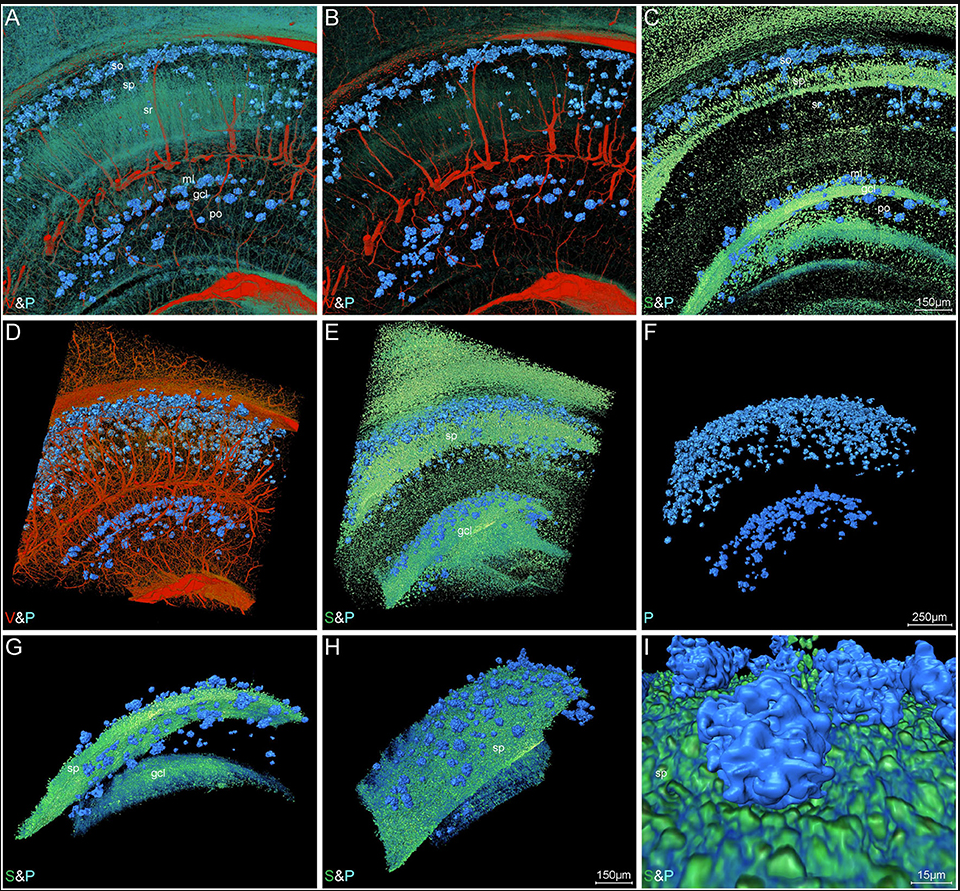
High-Resolution Digital Panorama of Multiple Structures in Whole Brain of Alzheimer's Disease Mice
Our study placed emphasis on solving problems in processing high-throughput bright field images and made attempt in developing a method for the extraction and reconstruction of multiple structures. This will facilitate a better understanding of the cerebral anatomical features under the pathological state of AD and shows extensive application prospect in drug efficacy assessment from brain-wide level.
Simultaneously visualizing Amyloid-β (Aβ) plaque with its surrounding brain structu... Read more
Xianzhen Yin, Xiaochuan Zhang, Jingjing Zhang, Weicheng Yang, Xian Sun, Haiyan Zhang, Zhaobing Gao, Hualiang Jiang
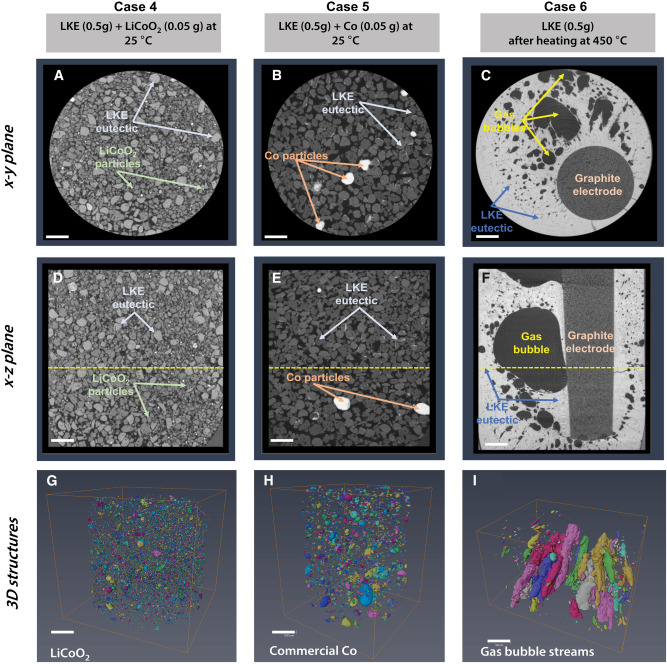
Recycling spent lithium-ion batteries (LiBs) guarantees the conservation of important metal resources by reducing demands on raw supply and offsetting the energy and environmental costs associated with its manufacture. Employing a molten salt as a solvent for extraction affords a much greener and simpler route to metal recovery by electrochemical means. The current mechanistic understanding of the electrochemical recovery of metals in molten salts needs to be improved for the process to be op... Read more
Mateen Mirza, Wenjia Du, Lara Rasha, Steven Wilcock, Arfon H. Jones, Paul R. Shearing, Dan J.L. Brett
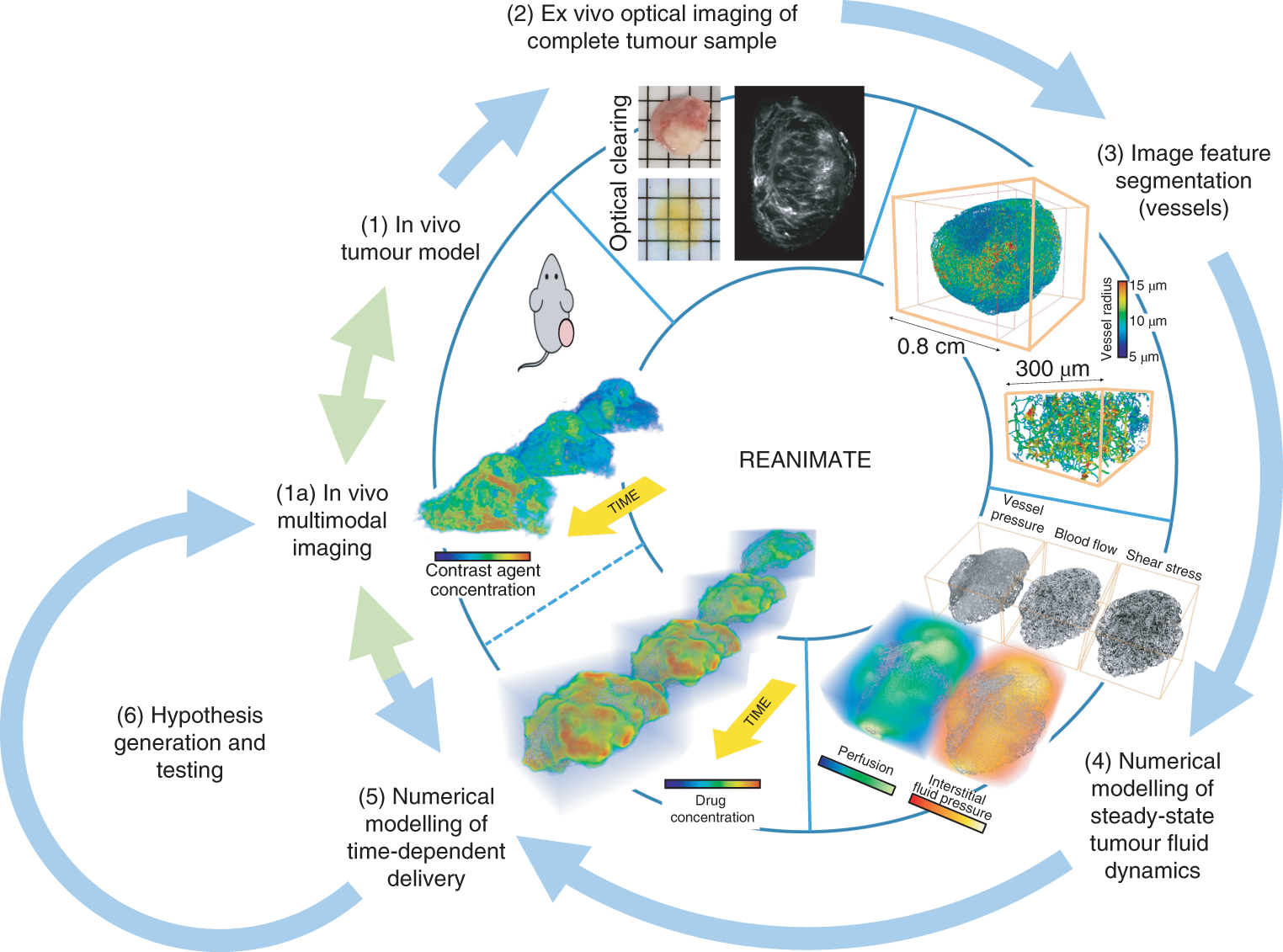
Understanding the uptake of a drug by diseased tissue, and the drug’s subsequent spatiotemporal distribution, are central factors in the development of effective targeted therapies. However, the interaction between the pathophysiology of diseased tissue and individual therapeutic agents can be complex, and can vary across tissue types and across subjects. Here, we show that the combination of mathematical modelling, high-resolution optical imaging of intact and optically cleared tumour tiss... Read more
Angela d’Esposito, Paul W. Sweeney, Morium Ali, Magdy Saleh, Rajiv Ramasawmy, Thomas A. Roberts, Giulia Agliardi, Adrien Desjardins, Mark F. Lythgoe, R. Barbara Pedley, Rebecca Shipley and Simon Walker-Samuel
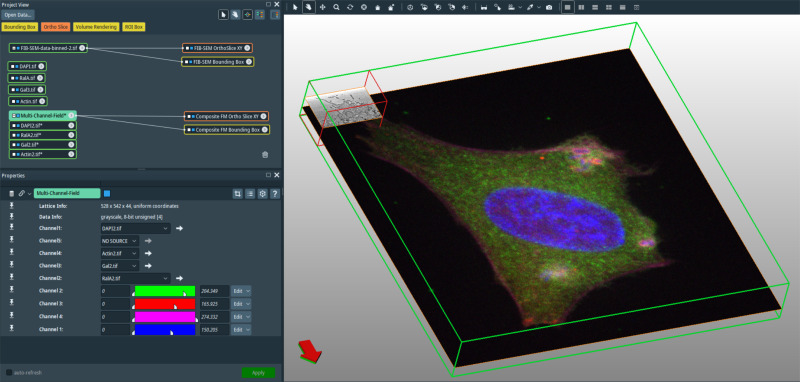
In recent years new methodologies and workflow pipelines for acquiring correlated fluorescence microscopy and volume electron microscopy datasets have been extensively described and made accessible to users of different levels. Post-acquisition image processing, and particularly correlation of the optical and electron data in a single integrated three-dimensional framework can be key for extracting valuable information, especially when imaging large sample volumes such as whole cells or tissu... Read more
Allon Weiner
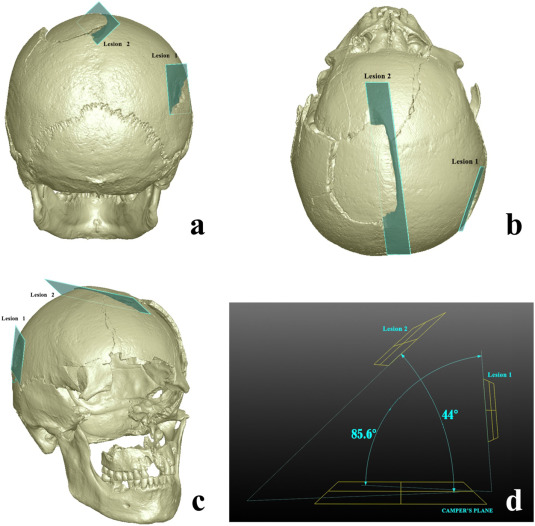
Human skeletal remains from archaeological contexts occasionally present signs of traumatic injuries from weapons, revealing, for example, the degree of interpersonal violence, the type of weapon and the sequence of events of a specific historical context.
Traumatic lesions are generally analyzed using macroscopic and microscopic methods, which are not necessarily integrated in the same study. In this study, we employed a multi-analytical approach to determine i... Read more
Antonino Vazzana, Lucia Martina Scalise, Mirko Traversari, Carla Figus, Salvatore Andrea Apicella, Laura Buti, Gregorio Oxilia, Rita Sorrentino, Silvia Pellegrini, Chiara Matteucci, Lucio Calcagnile, Raffaele Savigni, Robin N.M.Feeney, Giorgio Gruppioni, Stefano Benazziah
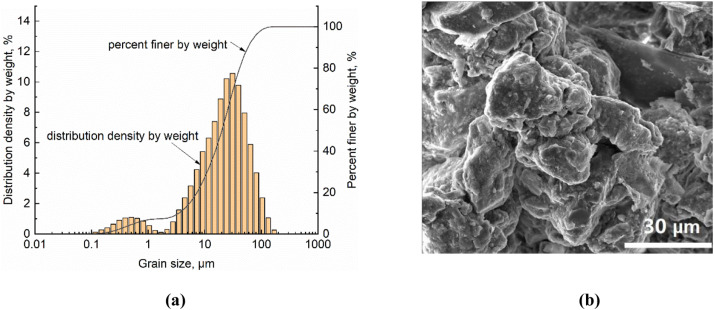
3D characterisation of the particle kinematics during loess collapse is performed based on X-ray micro-computed tomography.
Particle displacements and rotations associated with the collapse are determined.
The volumetric strain is shown to be significantly heterogeneous at single-particle scale.
The evolution of particle-to-particle contacts is found to be much more complex than previously stated.
An apparatus is specially designed to perf... Read more
B. Yu, W. Fan, J.H. Fan, T.A. Dijkstra, Y.N. Wei, T.T. Wei
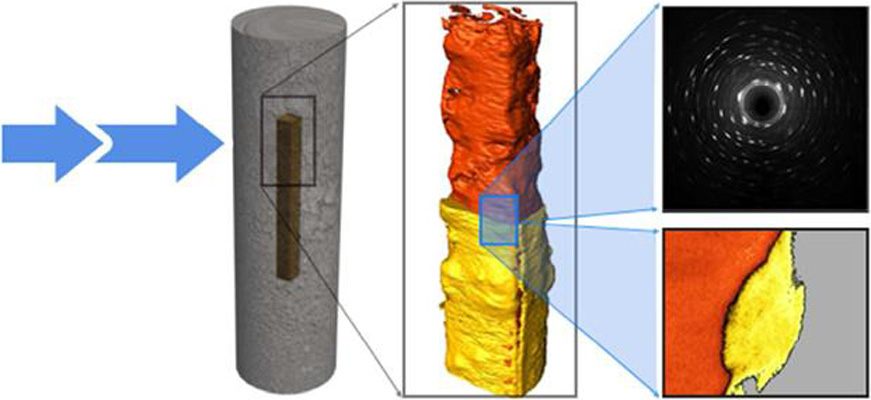
Nuclear waste viewed in a new light; a synchrotron study of uranium encapsulated in grout
How do you characterise the contents of a sealed nuclear waste package without breaking it open?
This question is important when the contained corrosion products are potentially reactive with air and radioactive. Synchrotron X-rays have been used to perform micro-scale in-situ observation and characterisation of uranium encapsulated in grout; a simulation for a typical intermediate level waste storage packet. X-ray tomography and X-ray powder diffraction generated both qualitative and ... Read more
C.A. Stitt, M. Hart, N.J. Harker, K.R. Hallam, J. MacFarlane, A. Banos, C. Paraskevoulakos, E. Butcher, C. Padovani, T.B. Scott
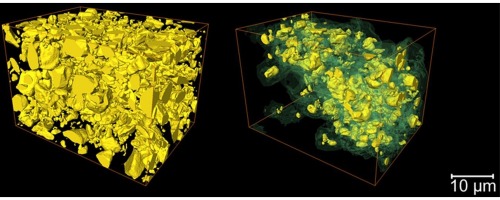
The microstructural degradation of a composite silicon electrode at different stages in its cycle life was investigated in 3D using X-ray nano-computed tomography. A reconstructed volume of 36 μm × 27 μm × 26 μm from the composite electrode was imaged in its pristine state and after 1, 10 and 100 cycles. Particle fracturing and phase transformation was observed within the electrode with increased cycling. In addition, a distinct, lower X-ray attenuating phase was clearly resolved,... Read more
Oluwadamilola O. Taiwo, Melanie Loveridge, Shane D.Beattie, Donal P.Finegan, Rohit Bhagat, Daniel J.L.Brett, Paul R.Shearing
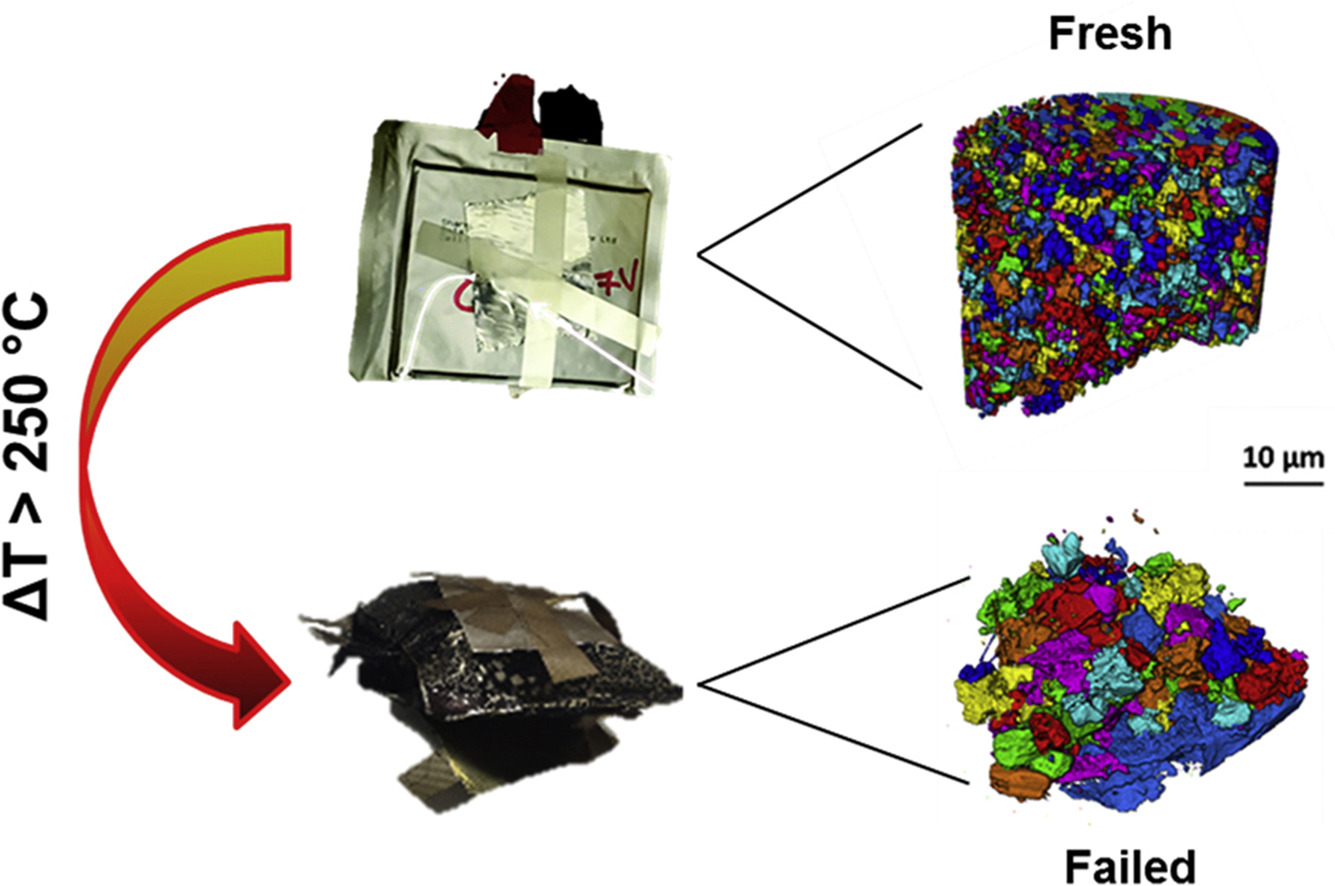
Multiscale tomographic analysis of the thermal failure of Na-Ion batteries
In recent years, the ability to examine the processes that cause the catastrophic failure of batteries as a result of thermal runaway has improved substantially. In this work, the effect of thermal runaway on the microstructure of the electrodes of a Na-ion battery is examined using X-ray computed tomography for the first time. The thermal failure induced via accelerating rate calorimetry enabled the examination of failed electrodes, which were subsequently compared with fresh s... Read more
Robinson, J. B., Heenan, T. M. M., Jervis, J. R., Tan, C., Kendrick, E., Brett, D. J. L., & Shearing, P. R.
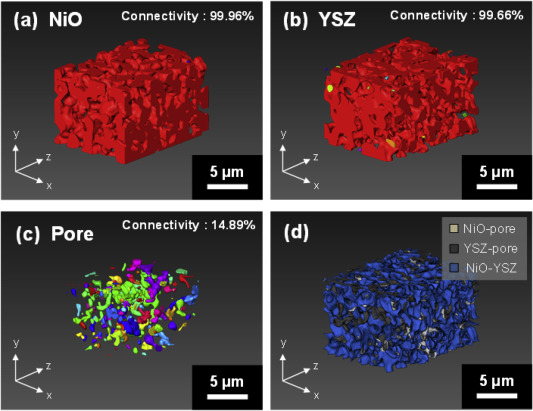
Nickel-yttria-stabilized zirconia (Ni-YSZ) cermet is widely used as an anode material in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs); however, Ni re-oxidation causes critical problems due to volume expansion, which causes high thermal stress. We fabricated a Ni-YSZ anode functional layer (AFL), which is an essential component in high-performance SOFCs, and re-oxidized it to investigate the related three-dimensional (3D) microstructural and thermo-mechanical effects. A 3D model of the re-oxidized AFL ... Read more
Jun Woo Kim, Kiho Bae, Hyun Joong Kim, Ji-won Son, Namkeun Kim, Stefan Stenfelt, Fritz B. Prinz, Joon Hyung Shim
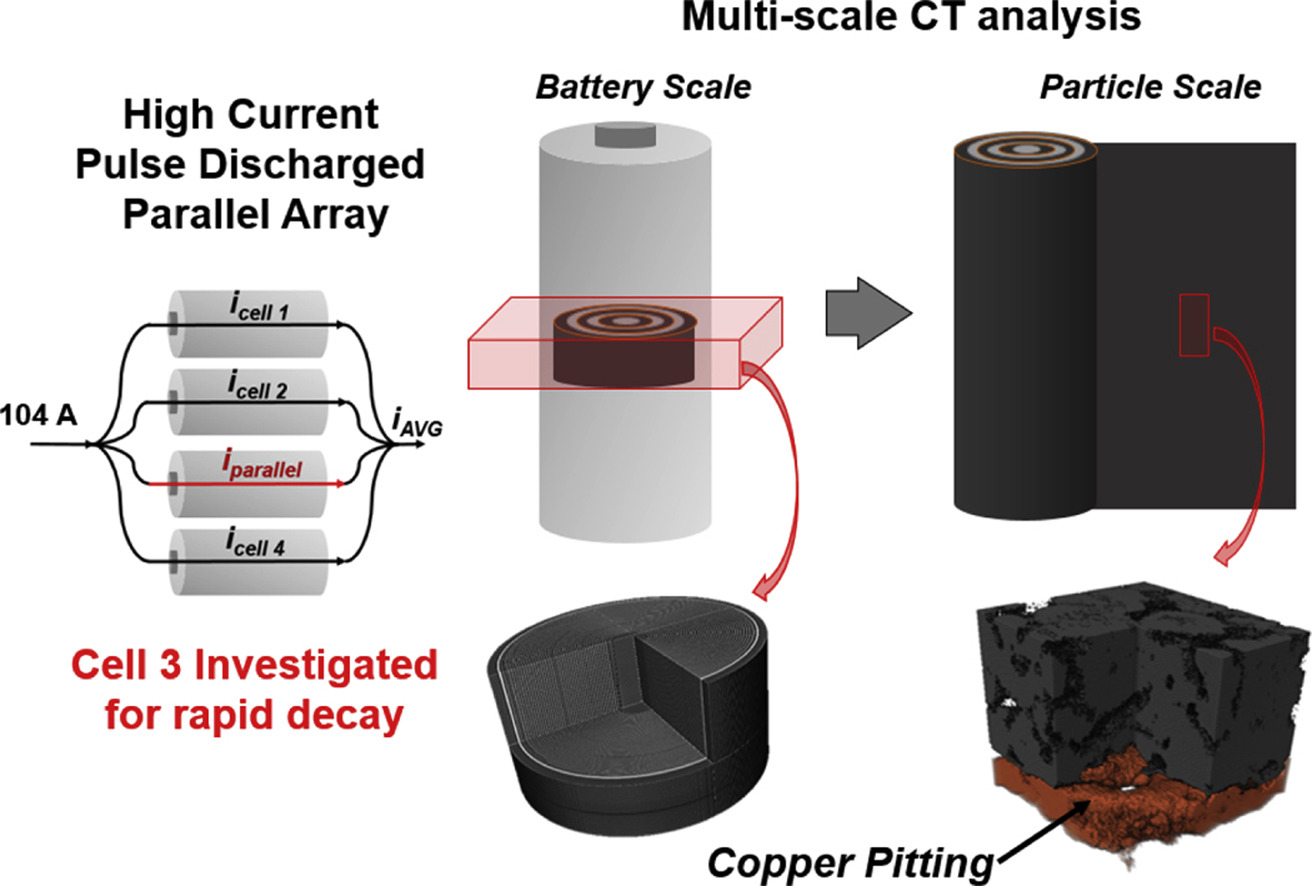
X-ray computed tomography (X-ray CT) across multiple length scales is utilized for the first time to investigate the physical abuse of high C-rate pulsed discharge on cells wired individually and in parallel.. Manufactured lithium iron phosphate cells boasting high rate capability were pulse power tested in both wiring conditions with high discharge currents of 10C for a high number of cycles (up to 1200) until end of life (<80% of initial discharge capacity retained). The parallel ass... Read more
Rachel Carter, Brett Huhman, Corey T. Love, Iryna V. Zenyuk
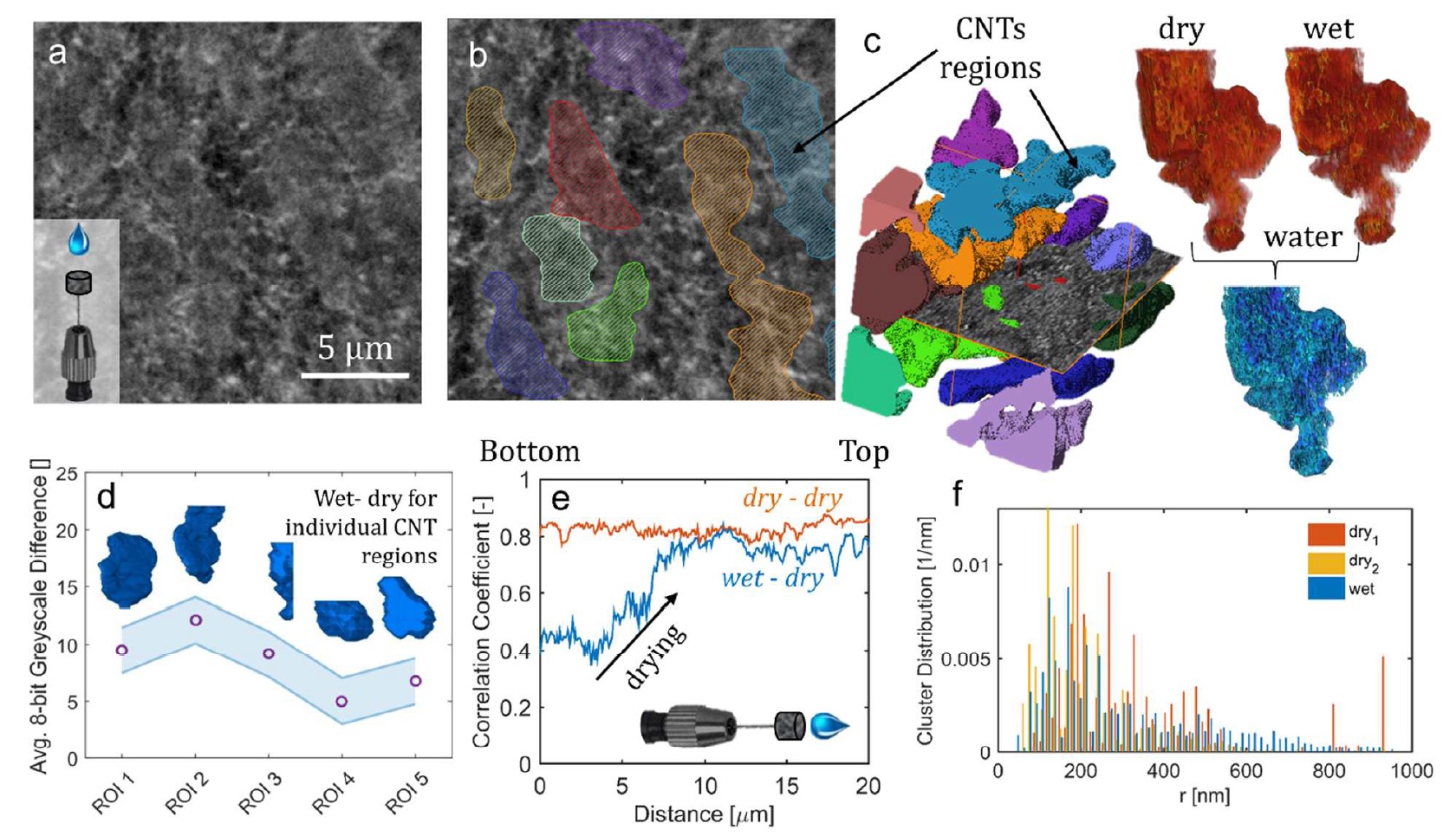
This work describes the performance improvement of a polymer electrolyte fuel cell with a novel class of microporous layers (MPLs) that incorporates hydrophilic additives: one with 30 μm aluminosilicate fibers and another with multiwalled carbon nanotubes with a domain size of 5 μm. Higher current densities at low potentials were observed for cells with the additive-containing MPLs compared to a baseline cell with a conventional MPL, which correlate with improvements in water management. Th... Read more
Dusan Spernjak, Rangachary Mukundan, Rodney L. Borup, Liam Connolly, Benjamin Zackin, Vincent De Andrade, Michael Wojcik, Dilworth Y. Parkinson, David Jacobson, Daniel Seth Hussey, Karren L More, Thomas Chan, Adam Z Weber, and Iryna V. Zenyuk
Cryo-STEM mapping of solid–liquid interfaces and dendrites in lithium-metal batteries
Solid–liquid interfaces are important in a range of chemical, physical and biological processes but are often not fully understood owing to the lack of high-resolution characterization methods that are compatible with both solid and liquid components. For example, the related processes of dendritic deposition of lithium metal and the formation of solid–electrolyte interphase layers are known to be key determinants of battery safety and performance in high-energy-density lithium-metal bat... Read more
Michael J. Zachman, Zhengyuan Tu, Snehashis Choudhury, Lynden A. Archer & Lena F. Kourkoutis
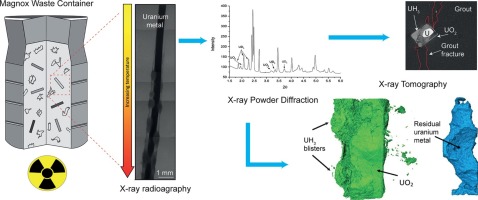
To accurately predict the initiation and evolution of uranium hydride potentially present in nuclear waste containers, studies of simulated conditions are required.
Here, for the first time, the uranium-deuterium reaction was examined in-situ, in real time, whilst within grouted media. A deuterium gas control rig and stainless steelquartz glass reaction cell were configured on a synchrotron beam line to collect X-ray diffraction and X-ray tomography data. It was found that deuteride fo... Read more
C.A. Stitt, C. Paraskevoulakos, N.J. Harker, A. Banos, K.R. Hallam, C.P. Jones, T.B. Scott
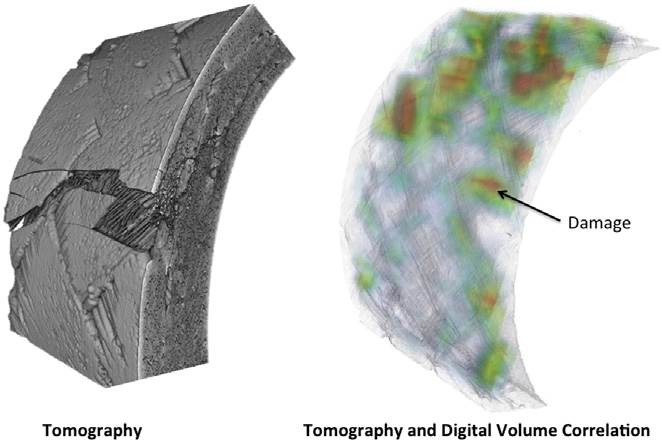
In situ observation of mechanical damage within a SiC-SiC ceramic matrix composite
SiC-SiC ceramic matrix composites are candidate materials for fuel cladding in Generation IV nuclear fission reactors and as accident tolerant fuel clad in current generation plant.
Experimental methods are needed that can detect and quantify the development of mechanical damage, to support modelling and qualification tests for these critical components. In situ observations of damage development have been obtained of tensile and C-ring mechanical test specimens of a braided nuclear gr... Read more
L. Saucedo-Mora, T. Lowe, S. Zhao, P.D. Lee, P.M. Mummery, T.J. Marrow
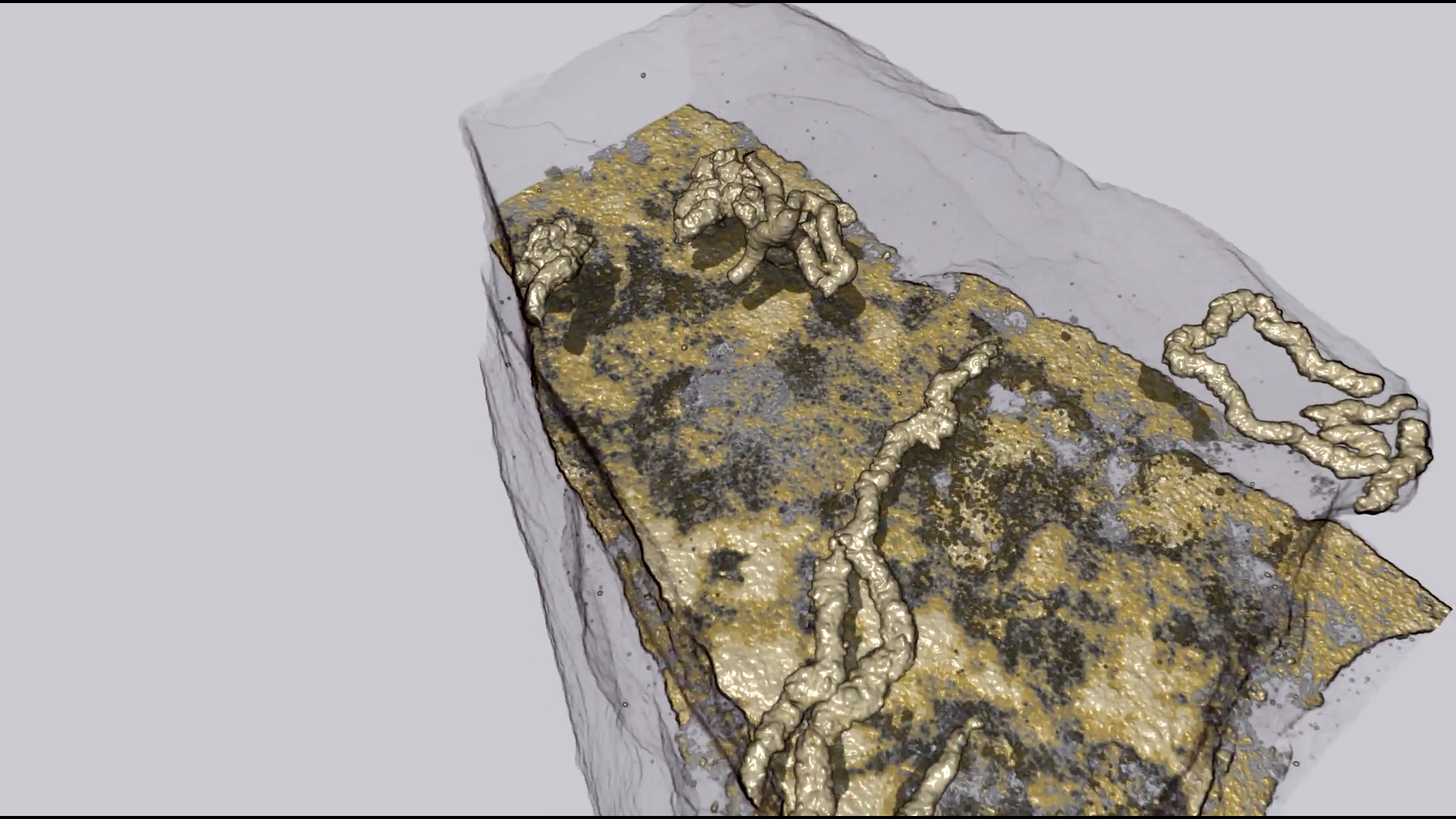
Organism motility in an oxygenated shallow-marine environment 2.1 billion years ago
Evidence for macroscopic life in the Paleoproterozoic Era comes from 1.8 billion-year-old (Ga) compression fossils [Han TM, Runnegar B (1992) Science 257:232–235; Knoll et al. (2006) Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 361:1023–1038], Stirling biota [Bengtson S et al. (2007) Paleobiology 33:351–381], and large colonial organisms exhibiting signs of coordinated growth from the 2.1-Ga Francevillian series, Gabon. Here we report on pyritized string-shaped structures from... Read more
Abderrazak El Albani, M. Gabriela Mangano, Luis A. Buatois, Stefan Bengtson, Armelle Riboulleau, Andrey Bekker, Kurt Konhauser, Timothy Lyons, Claire Rollion-Bard, Olabode Bankole, Stellina Gwenaelle Lekele Baghekema, Alain Meunier, Alain Trentesaux, Arnaud Mazurier, Jeremie Aubineau, Claude Laforest, Claude Fontaine, Philippe Recourt, Ernest Chi Fru, Roberto Macchiarelli, Jean Yves Reynaud, François Gauthier-Lafaye, and Donald E. Canfield
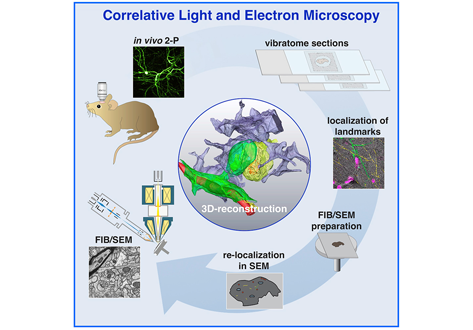
Label-free 3D-CLEM using endogenous tissue landmarks
We demonstrate feasibility of the workflow by combining in vivo 2-photon microscopy and focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy (FIB/SEM) to dissect the role of astrocytic coverage in the persistence of dendritic spines.
Emerging 3D correlative light and electron microscopy (CLEM) approaches enable studying neuronal structure-function relations at unprecedented depth and precision. However, established protocols for the correlation of light and electron micrographs rely ... Read more
Manja Luckner,Steffen Burgold, Severin Filser, Maximilian Scheungrab, Yilmaz Niyaz, Eric Hummel, Gerhard Wanner, Jochen Herms
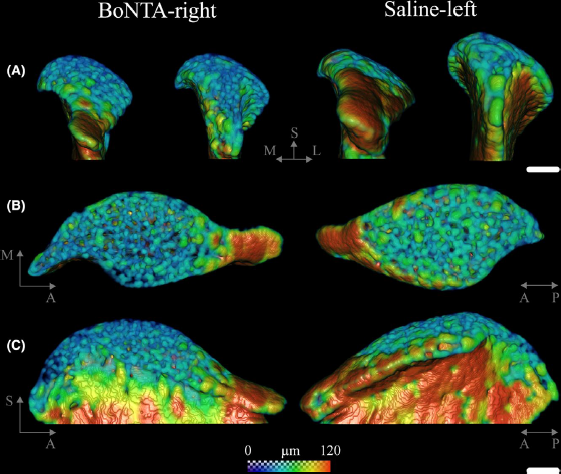
Masseter muscle function influences mandibular bone homeostasis. As previously reported, bone resorption markers increased in the mouse mandibular condyle two days after masseter paralysis induced with botulinum toxin type A (BoNTA), followed by local bone loss.
This study aimed to evaluate the bone quality of both the mandibular condyle and alveolar process in the mandible of adult mice during the early stage of a BoNTA‐induced masseter muscle atrophy, using a combined 3D histomorpho... Read more
Julián Balanta‐Melo, María Angélica Torres‐Quintana, Maximilian Bemmann, Carolina Vega, Constanza González, Kornelius Kupczik, Viviana Toro‐Ibacache, Sonja Buvinic
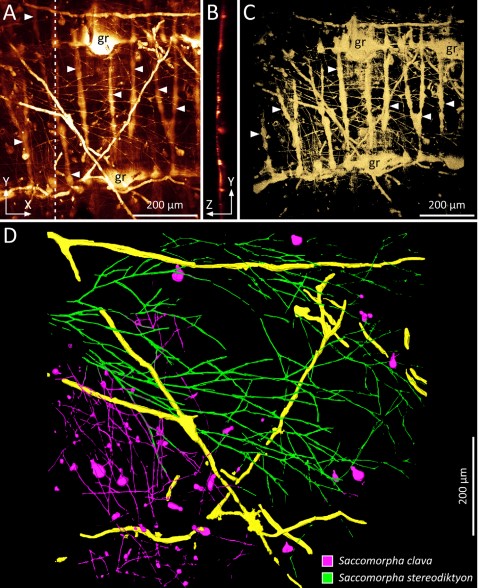
Microscopic organisms that penetrate calcareous structures by actively dissolving the carbonate matrix, namely microendoliths, have an important influence on the breakdown of marine carbonates.
Microscopic organisms that penetrate calcareous structures by actively dissolving the carbonate matrix, namely microendoliths, have an important influence on the breakdown of marine carbonates. The study of these microorganisms and the bioerosion traces they produce is crucial for understanding ... Read more
Philipp-Konrad Schätzle, Max Wisshak, Andreas Bick, André Freiwald, Alexander Kieneke